Cloud Architectures Microservice Architecture vs Monlithic Architecture
There are millions of running application today most of which have been developed using a monolithic architecture. With the rise of IoT & Big Data, most of the infrastructure will be in the cloud to save on cost, increase delivery and give room for horizontal scaling.
Horizontal scalability is the ability to increase capacity by connecting multiple hardware or software entities so that they work as a single logical unit.
With this challenge, majority of the companies need to change the architecture of their applications to utilize the latest technologies that give room for scaling, easy management as well as save on cost by minimizing the use of local data centers.
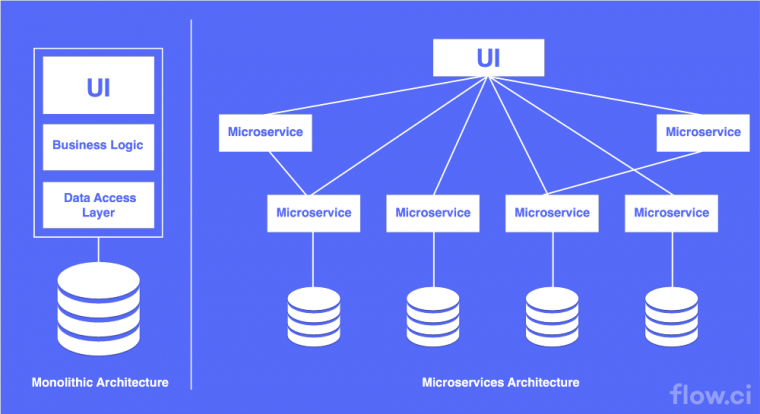
Monolithic Architecture
A monolithic architecture is the traditional unified model for the design of a software program. This means that the application has single code base with multiple modules. Mostly this is divided into tiers/ layers such as presentation layer, business layer and database layer.
Companies that own these systems have developed the applications for a long time and as change requests increase and need to add new modules in to the application, it has become very difficult to manage these applications.
Monolithic architectures bring some challenges and makes it difficult to leverage on the new technologies that can reduce cost, increase performance, and scale your application.
Microservice Architecture
Microservice architecture is an approach of building large enterprise application with multiple small unit called service. Each service can be developed, deployed and tested individually. Each service intercommunicate with a common communication protocol like REST web service with JSON, HTTP or HTTPS.
Each service run individually either in single machine or different machine but they execute their own separate process. This makes it possible to specify the resources (CPU and RAM) that each microservice can consume. It is also easy to scale up the resources through horizontal scaling in the cloud.
Each service may have its own database or storage system or they can share common database or storage system. This means that if one service has a bug that makes it to go down, it does not affect other services and other services of the application can continue operating. Microservice architecture is all about breaking down a monolithic application into small chunks that work together(Services). Taking an example of an e-commerce web application, it can be divided into microservices as follows.
- User management service - Handles user registration and authentication
- Shopping cart service - Manages the shopping cart
- Stock service - Manages the goods in stock
- Payment service - Manage billing of goods
- Recommendation service - To recommend goods to visiting users
Advantages of Microservices Over Monolithic Applications
- In monolithic applications, the code base grows very fast making it very difficult to understand and manage. Each microservice can be managed individually and does not contain a large code base.
- Scaling a monolithic application is challenging while microservices can be scaled by provisioning more resources to individual application that need to scale.
- In a monolithic application, continuous deployment and integration becomes challenging due to the increasing code base. Testing and debugging code is also very complicated which slows down the development cycle. Since microservicess are decoupled, it is easy to set up continuous delivery for each microservices making it easy and efficient to respond to change requests.
- A monolithic application can only be in one single language. Microservices can be developed in different languages which makes it efficient because a developer can benefit from the capabilities of different languages for certain features _eg: Python for data analytics and machine learning in an e commerce website. _
- Code integration in a monolithic application is difficult because different teams are working on the same code base. If one team pushes code with a bug into production, the whole system goes down. With microservices, you can deploy small teams to work on each of the microservices making deployment and debugging easier.
There are a couple of tools that can help you develop and manage microservices easily such as Java EE, Spring Boot (I will discuss this in a later blog), Apache Spark and AWS Lambda among many more.
Disadvantages of Microservices
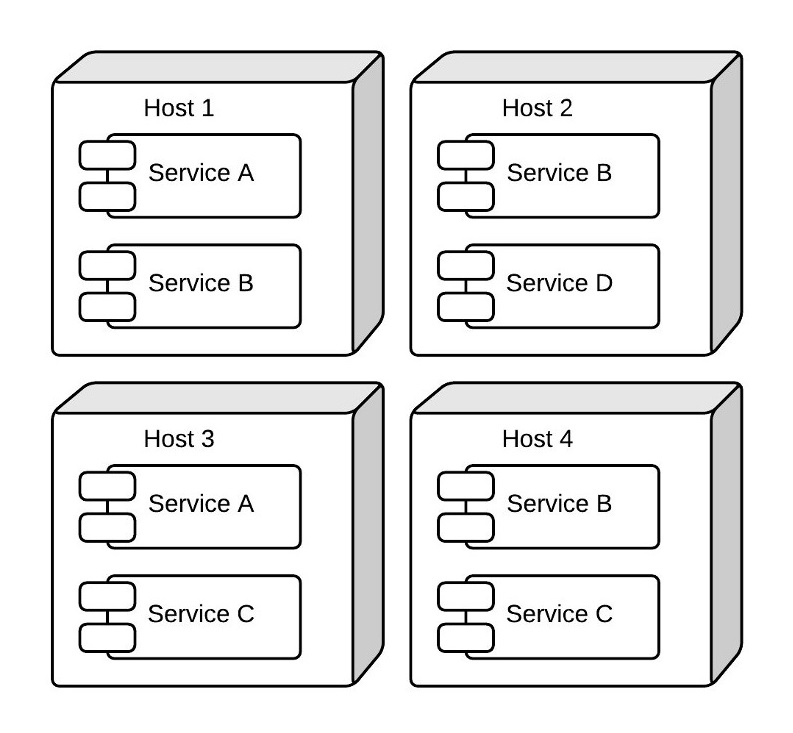
Though microservices are a powerful tool for your application, they have their disadvantages as well. Because services will be spread across multiple hosts, it can be difficult to keep track of which hosts are running certain services. Also, even though each host may not be as powerful as the host running the monolithic application, as the microservices architecture scales out, the number of hosts will grow faster than it will with a monolithic architecture. This results in over-provisioning and increased costs. If services are implemented in different programming languages, this means the deployment of each service will require a completely different set of libraries and frameworks, making deployment to a server complex.
Nevertheless these challenges can be solved using Docker together with other container management technologies such as kubernetes, DockerHub and Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS).
I hope you enjoyed this blog. Watch out for the next blog where I will be discussing on how to use docker for microservices.
To make a comment you have to login

0 Comments